
DESCRIPTION
Welcome to EFFECTIVE, a 4-year Horizon Europe project with the mission to protect and restore the EU’s Mediterranean Blue Natural Capital. By combining cutting-edge science, technological nature-based solutions, digitalization, and social implications, we will create a comprehensive knowledge base and practical guidance for ecosystem-based management.
Join us on this transformative journey, where innovation meets nature’s embrace. Together, we can shape a future where coastal and marine ecosystems thrive, and the blue natural capital flourishes for generations to come.
OBJECTIVES
Our primary objective is to develop a comprehensive scientific knowledge base and practical guidance, combining science, technological nature-based solution, digitalization, and social implication for the application of the Ecosystem-Based management to the protection and restoration management of the EU’s Mediterranean Blue Natural Capital.
In order to achieve our main objective, we have identified the following specific objectives:
- Apply EBMS to identify, analyse and extend an ecological corridor in the Mediterranean Sea, connecting habitats and biodiversity.
- Apply EBMS to analyse and extend the status of four Marine Protected Areas in the Mediterranean Sea.
- Demonstrate four nature-based seabed protection and restoration solutions, including preserving seabed carbon sequestration capacity, in a real environment.
- To identify limiting factors, gaps and recommendations of existing MPA legislation regarding environmental and anthropogenic pressures, setting up links with previous projects.
- To implement an innovative digital data visualisation and aggregation tool in the form of a Digital Twin for enabling data exploration, research, participation and citizen science.
EFFECTIVE Pilot Areas
EFFECTIVE provides the implementation of the EBMS in four pilot areas towards protection and restoration solutions,
besides taking into account the connectivity between three of them through the existing Cetacean Migration Corridor.
Pilot area 1 - Mar de L’Empordà (Western Med)
– is a biodiversity hotspot in Spain with seven Marine Protected Areas. Governed by the Taula de Cogestió Marítima del Litoral del Baix Empordà, it involves stakeholders from various sectors. The area showcases diverse ecosystems with notable species like red coral, gorgonians, seagrasses, sponges, noble pen shell, seahorses, and antennae gobies.

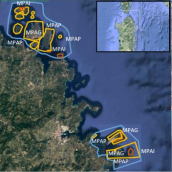
Pilot area 2 - Ebro Delta Bays (Western Med)
– is a vital Marine Protected Area and Natura 2000 protected zone in Spain. It encompasses unique habitats and species, including seagrass beds, coastal lagoons, and salt marshes. Despite its ecological significance, the area faces water quality challenges, struggling to meet the standards of the Water Framework Directive and the Marine Strategy for transitional and coastal waters.
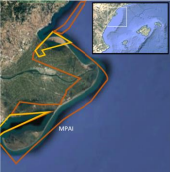
Pilot area 3 - Sardinia Septentrional (Central-Western Med)
– La Maddalena Archipelago National Park, Tavolara-Punta Coda Cavallo MPA, and Archipelago Toscano National Park in Northeastern Sardinia, Italy. These areas are under distinct protected designations. All areas harbor essential habitats such as coralligenous formations and Posidonia oceanica meadows.
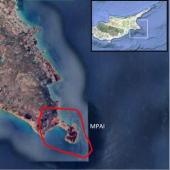
Pilot area 4 - Cavo Greco (Eastern Med.)
– is part of the Natura 2000 network. Known for its rich biodiversity, the area features invertebrate species like Cystoseira spp. and Sargassum vulgare, along with coralligenous biocenosis housing various sponge species. Notably, it hosts endangered and vulnerable coral species, C. caespitosa and D. ramea, endemic to the Mediterranean Sea, facing threats from human activities, climate change, and extreme weather events.
WORKPLAN
































